Objective - Study of character of specimen and identification with reason -- Amoeba, Hydra, liver fluck, ascaris, leech earthworm, prawn ,silkworm, honeybee ,Snail, starfish, Shark, rohu, frog ,calotes (lizard) pigeon rabbit.
REQUIREMENTS
Fresh or preserved animal specimens, record file, pencil, eraser, sharpener, rular, a laboratory guide
or practical book.
PROCEDURE
1.Come prepared in the class for the study of animal specimens.
2.Listen carefully the instructions imparted to you by the teacher and note down the important identifying features told to you.
3. Observe and study the specimens or slide.
4.Draw directly from the specimen or slide showing all the details by taking appropriate scale of magnification.
5. Draw only what is visible to you. Do not sketch the elaborate diagrams from the book.
6.Take the help of practical guide book to check the correctness of the diagram and labelling its various parts.
7.Label the diagram symmetrically with straight parallel lines.
8. Por a specimen give classification on the top of the diagram towards right side.
1.AMOEBA PROTEUS
Classification
Kingdom-protista
Phylum Protozoa
Class- Sarcodina
Order--Amoebida
Genus-Amoeba
Species-Proteus
Comments
1. Amoeba occurs in ponds, ditches, lakes, streams ete. having plenty of decaying organic matter.
2. It is unicellular, microscopic, grayish in colour and is about 0.2 to 0.5 mm in diameter.
3. Under the microscope, a living Amoeba
appears like an irregular jelly like, tiny mass of hyaline protoplasm. The protoplasm can be distinguished into an outer ectoplasm and inner endoplasm.
4. The endoplasm contains food vacuoles,
contractíle vacuole anda prominant nucleus.
5. The outline of body continues changing due to the formation of small finger like out growths called pseudopodia. These are the organs of locomotion.
Pseudopodia also help in food capture.
6. Amoeba exhibits holozoic mnde of nutrition. It ingests all kinds of aquatic microorganisms like bacteria,diatoms, algae ete.
7. It reproduces asexually by binary fission and multiple fission (sporulation)
8. It passes unfavourable conditions by forming a protective cyst covering around it.
Diagnostic Features
1.Unicellular and irregular shape of the body.
2.Presence of finger like and blunt pseudopodia.
3.Presence of contractíle vacuole.
2. HYDRA
Classification
Kingdom- Animalia
Phylum- Cnidaria
Class- Hydrozoa
Order- Hydroida
Genus- Hydra
Species-vulgaris
Comments
1. Hydra is found in clear and cool fresh water ponds, pools, lakes,streams etc. Most of the times it remain attached to submerged stones, vegetation and other objects, by means of its basal end. Some-
times it gets detached from the substratum and move about in water in different ways like floating, looping, somersaulting and gliding.
2.The body consists of an elongated tube with closed base and single opening at oral (mouth) end. The dialated region around mouth called hypostome, bears 6 to 10 finger like hollow projections, the tentacles.They are highly contractile and are used for catching food and for locomotion.
3.The body wall consists of two layers of cells (diploblastic animal).The outer is epidermis and inner is gastrodermis. Between them is present non-cellular, jelly like material called mesoglea.
4.The epidermis contains stinging cells or cnidocytes, to act as organs of defence and offence.
5. Reproduction takes place asexually by budding and sexually by gametes, produced by the gonads (testis and ovary) present at the body wall.
Diagnostic Features
1. Soft bodied and diploblastic.
2.Body is elongated and sac like.
3.Presence of tentacles and stinging cells.
3. FASCIOLA HEPATICA (Liver fluke)
Classification
Kingdom- Animalia
Phylum- Platyhelminthes
Class-Trematoda
Order- Echinostomida
Genus- Fasciola
Species- hepatica
- Platyhelminthes
Comments
1. It is an endoparasite found in the bile ducts of sheeps, goats, cattles and sometimes other vertebrates including man. It causes a serious liver disease called liver rot.
2. It is somewhat triangular, flat, leaf like parasite about 25 mm in length. It has an oral and ventral sucker (acetabulum) used to adhere to the bile duct.
3.The body is covered by cuticle with spinules.
4.It has blind sac body plan with single opening called mouth.
5.The animal is hermaphrodite and has a common genital aperture or gonopore in front of acetabulum.
6.It has a complicated, double host (digenetic) life cycle. The secondary host is snail.
7.F. gigantica is a larger species of liverfluke, commonly found in the liver of cattles.
Diagnostic Features
1. The body is triangular and leaf like.
2. Body is covered with cuticle.
3. Presence of two suckers.
4. ASCARIS LUMBRICOIDES (Round worm)
Classification
Kingdom- Animalia
Phylum- Nemathelminthes
Order- Ascaroidea
Genus-Ascaris
Species-lumbricoides
Comments
1. It is a common intestinal parasite of man especially children. Occasionally it may occur in the intestine of bold pigs, sheep, cattle, monkey etc.
2. It has a cylindrical body with tapering ends.
3.The front end of body has a terminal triradiate mouth surrounded by three lips. a little behind anterior end . there is a small excretory pore.
4. The adult worms are sexually dimorphic male comparatively smaller than female. there posterior part is slightly curved. Male have two needle like penial setae Or copulatory setae which protrude out from their anus.
Diagnostic Features
1.Endoparasite.
2.Elongated body with tapering ends.
3. Body is covered with cuticle.
4. Mouth is guarded by three lips.
5. HIRUDINARIA GRANULOSA (Leech)
Classification
Kingdom Animalia
Phylum- Annelida
Class- Hirudinea
Order- Gnathobdellida
Genus- Hirudinaria
Species- granulosa
Comments
1.It is found in ponds, lakes, rivers, swamps etc. and in the moist soils near such water bodies.
2.It is a facultative ectoparasite of cattle and other mammals. It sucks blood (sanguivorous) by periodically coming in contact with the body of the host.
3.Its body is somewhat dorso-ventrally flattened and measures about 15 cm. in length but it can stretch its length upto 30 cm., when required. It is olive green in colour.
4. The body is divided into 33 segments and each segment has superficial 2 to 5 annuli (rings).
5.The anterior part of the body is narrower and bears a ventral triradiate mouth surrounded by a cup like anterior sucker.
6.The posterior end bears a larger posterior sucker, and a mid-dorsal anus just in front of the sucker. The suckers help in locomotion, and in adhering to the body of host during blood meal.
7. Leech is hermaphrodite animal but shows cross fertilization.
Diagnostic Features
1. Slimy, elongated and segmented body.
2. Presence of anterior and posterior suckers.
6. PHERETIMA POSTHUMA (Earth worm)
Classification
Kingdom- Animalia
Phylum- Annelida
Class- Oligochaeta
Order- Terricolae
Genus- Pheretima
Species-posthuma
Comments
1.Earthworms live in burrows in moist soils where decaying vegetation and other organic matter is present.During rainy season they come out of their burrows as the latter get flooded by water.
2.It has a long cylindrical and segmented body. It measures about 10-20 cm. in length. It is quite slimy in touch and pinkish brown in colour.
3.The dorsal surface of the body is recognised by its darker colour and ventral surface is marked by genital apertures and papillae located in the anterior region of the body.
4.The segments 14th, 15th and 16th form a band called clitellum. It forms one or more egg cases or cocoons in which ova are laid and fertilized.
5. Mouth is present at the enterior end. A fleshy lobe called prostomium dorsally over hangs upon the mouth like a hood. Anus is present in the last segment.
6. Each segment except the first and the last bears row of minute yellowish setae for locomotion.
7.Earthworm is hermaphrodite animal but shows cross fertilization.
Diagnostic Features
1.Elongated, cylindrical and segmented body.
2. Presence of prostomium and clitellum.
3.Presence of setae for locomotion.
7. PALAEMON
Classification
Kingdom- Animalia
Phylum- Arthropoda
Class Crustacea
Order- Decapoda
Genus- Palaemon
Species- malcolmsonii
Comments
1. It occurs in fresh waters such as in rivers, ponds, lakes and swamps.
2. The body is curved and is about 5 to 18 cm. long. It is distinguished into cephalothorax and a long abdomen.
3. The cephalothorax is dorsally covered by a hard carapace, which extends as a serrated process called rostrum.
4.Cephalothorax bears eight pairs of segmented legs and on pair each of antennae, antennules and stalked compound eyes.
5. Abdomen consists of six segments, with one pair of paleopod each used for swimming.
6. Prawns are unisexual i.e., male and female sex organs occur in separate individuals.
Diagnostic Features
1. Brown coloured, spindle shaped and curved body.
2. Cephalothorax is covered by a carapace with serrated rostrum.
3. Abdomen six segmented.
8. BOMBYX MORI (Silk worm)
Classification
Kingdom-Animalia
Phylum- Arthropoda
Class- Insecta
Order- Lepidoptera
Genus- Bombyx
Species-mori
Comments
1. The adult silk moth is about 2.5 cm. long with two pairs of wings. It is creamy white in colour.
2.The body is divisible into head, thorax and abdomen and is covered by minute scales.
3.Silk worms are unisexual. Female moth lays three to five hundred eggs in clusters upon the leaves of mulberry
4.The life cycle of the moth comprises of four stages : Egg→ Larva → Pupa → Adult.
5. The larva undergoes four moults and then stop feeding. It secretes a sticky fluid through its spinnerets,which on coming in contact with air become silk thread and remains wrapped around its body to form pupa.
6. The pupa hatches out into an adult moth.
Diagnostic Features
1. Body is divisible into head, thorax and abdomen.
2.Presence of two pairs of wings and three pairs of legs.
3.Larva form cocoon.
9. APIS INDICA (Honey bee)
Classification
Kingdom- Animalia
Phylum- Arthropoda
Class Insecta
Order Hymnoptera
Genus- Apis
- Arthropoda
Species- indica
Comments
1.The honey bee is a social insect and lives in a colony showing great division of labour.
2. Three types of individuals i.e., queen,drones and workers are found in a colony. The drones are the males,while the workers are sterile females.The queen lays eggs.
3.The body of honey bee is divided into head, thorax and abdomen.
4. The head bears a pair of antennae and a pair of compound eyes.
5. Thorax has three pairs of legs and two
pairs of wings.
6.The mouth parts are rasping and lapping type, modified for collecting the nectar and pollen. The worker bees have a sting at the posterior end of the body.
Diagnostic Features
1.Presence of jointed appendages.
2. Three pairs of legs and two pairs of wings, hind wings smaller.
10. PILA GLOBOSA (Apple snail)
Classification
Kingdom- Animalia
Phylum-Mollusca
Class-Gastropoda
-Mollusca
-Gastropoda
Order- Prosobranchiata
Genus- Pila
Species-globosa
Comments
1. It is commonly found in fresh water streams, ponds, ditches, lakes, rice fields etc. Though
it is aquatic but can live without water for quite some time.
2.It has a soft and slimy body enclosed in a coiled calcarious shell. The opening of the shell is closed by a thick plate like operculum.
3.The body is differentiated into head, food,
visceral mass and mantle.
4.The head overhangs the foot and bears two
pairs of tentacles and one pair of eyes.
5. The foot is anterior and ventral, sole like used
for creeping.
6. Sexes are separate with slight sexual dimorphism.
Diagnostic Features
1. Shell is univalved and coiled.
2. Foot muscular and broad.
3. Head distinct with eyes and tentacles.
11. ASTERIAS (Star fish)
Classification
Kingdom-Animalia
Phylum- Echinodermata
Class- Asterioda
Order- Forcipulata
Genus-Asterias
Species-rubens
Comments
1.It is a marine animal and is found crawling on rocky sea bottom in shallow water.
2.Its body is flattered, star shaped and pentamerous with a small central disc and five short and tapering radiating arms.
3.The oral surface directed downwards and bears pentagonal mouth in the central disc.
4.Aboral surface bears large number of short and movable spines. Anus is present in the centre of the disc.
5.A narrow ambulacral groove extends from each angle of the mouth along the midline of the oral surface of each arm. Each ambulacral groove contains on either side two rows of tubular retractile projections called tube feet or podia. The latter are connected with water vascular system and help in locomotion, food capture and respiration.
6.Sexes are separate without sexual dimorphism.
Diagnostic Features
1. Body pentagonal and star shaped.
2.Oral and aboral surfaces are quite distinct.
3.Each arm with four rows of tube feet.
12. SCOLIODON (Dog fish/shark)
Classification
Kingdom-Animalia
Phylum- Chordata
Sub-phylum- Vertebrata
Class-Chondrichthyes
Genus- Scoliodon sp.
Comments
1. Dog fish commonly known as the shark, is found in the coastal waters of India.
2. It has somewhat laterally compressed and spindle shaped or steamlined body with pointed snout. The body is differentiated into head, trunk and tail.
3.The head is dorso-ventrally compressed, which ventrally bears the semi-circular mouth with sharp inwardly curved and pointed teeth. Two large eyes are present on the head. Five vertical gill clefts are present behind each eye.
4. Two mid-dorsal, one mid-ventral, one caudal and two pairs of lateral (pectoral and pelvic) fins are present for swimming.
5. Sexes are separate. The males have claspers in pelvic region. These are copulatory organs.
6.Sharks are viviparous i.e., give birth to young ones.
13. LABEO ROHITA (Rohu)
Classification
Kingdom Animalia
Phylum Chordata
Sub-phylum- Vertebrata
Class-- Osteichthyes
Genus- -Labeo
Species rohita
Comments
1.It is a fresh water dweller commonly called rohu fish (the Indian carp), widely used as food fish in our country.
2.It measures about 30 to 90 cm. in length. The body is somewhat flattered and streamlined, dusky-black dorsally and laterally, but pale-white ventrally. It is covered with overlapping cycloid scales.
3.Mouth is sub-terminal and ventral. A pair each of nostrils and large lateral eyes without eyelids are present.
4.There are five pairs of gill slits coverd by an operculum.
5.Three median (dorsal, ventral and caudal) and paired pectoral and pelvic fins are present for swimming.The tail is homocercal (i.e., caudal
fin equally lobed).
6. Lateral line sense organs are
present.
7. Sexes are separate. The males are
without claspers.
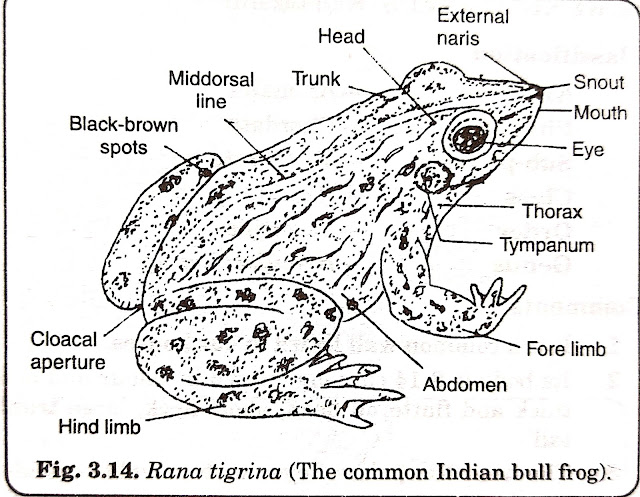
14. RANA TIGRINA (Frog)
Classification
Kingdom- Animalia
Phylum- Chordata
Sub-phylum- Vertebrata
Class- Amphibia
Order-Anura
Genus-Rana
Species- tigrina
Comments
1.It is commonly seen during rainy season in ponds, pools, lakes, river and humid places.
2.It has somewhat triangular, bilaterally symmetrical body with head and trunk.
3.The skin is dark green with black patches, moist
and is covered by mucus. The skin colour may change in accordance with the environment.
4.Eyes bulging upward without eyelid. Under wa-
ter, eyes are protected by a thin membrane called
nictitating membrane. A circular eardrum or tympanic membrane is located behind each eye.
5.The trunk bears two pairs of limbs. The hind limbs
are webbed and are longer than fore limbs. This helps in swimming and leaping.
6.Sexes are separate. Males have vocal sacs located a little behind the mouth. During breeding season males develop nuptial or copulatory pad on the first finger of fore limb.
15. CALOTES Sp. (Garden lizard)
Classification
Kingdom-Animalia
Phylum-Chordata
Sub-phylum- Vertebrata
Class- Reptilia
Genus-Calotes sp.
Comments
1.It is found on bushes and tree in gardens and fields. It is commonly known as 'girgit.
2.Its body is elongated and slender with an exoskeleton of over-lapping scales.
3.A crest of pointed and backwardly directed spines extends in the mid dorsal line from neck to tail.
4.The tail is long and slender.
5.The head is broad and distinct. The neck is red.
6.The limbs are pentadactyle and clawed.
7.It exhibits colour change when excited.
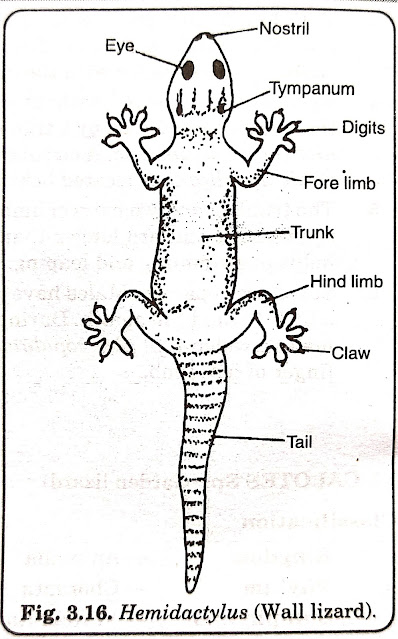
16. HEMIDACTYLUS (Wall Lizard)
Classification
Kingdom-Animalia
Phylum- Chordata
Sub-phylum- Vertebrata
Class- Reptilia
Order- Lacertilia
Genus-Hemidactylus sp.
Comments
1.It is a common wall lizard in our houses.
2.Its body is 8-14 cm long, brown in colour and is distinguished into thick and flattered head, short neck, large trunk and a 'tapering tail',
3.The head has pairs of eyes with movable eyelids, nostrils and ear openings.
4.The skin is dry, covered by minute scales. The tail with annular whorls of scales, which can be broken off (autotomy) on approach of an enemy.
5.Limbs four in number, each with five clawed digits. The limbs have adhesive vacuum pads, which help the lizard to move on the wall.
17. COLUMBA LIVIA (Pigeon)
Classification
Kingdom-Animalia
Phylum-Chordata
Sub-phylum- Vertebrata
Class-Aves
Genus- Columba
Species―livia
Comments
1. It makes its nests in scantily inhabited houses,
godowns, railway stations etc., and feeds upon, grains, fruits and insects.
2.Its body is 20 to 25 cm. long and covered with slate blue feathers. A narrow fluorescent bound occurs around the neck.
3.It has a sub spherical head, mobile neck, thick
trunk and short tail.
4.The beak is small and slightly curved in front. The
base of beak is covered by a lobe of fleshy skin called cese.
5.The eyes are red in colour.
6.Forelimbs are modified into feathered wings hav-
ing no digits. Hindlimbs are, covered with scales
and each bears four clawed digits. They are adapted for perching.
18. ORYCTOLAGUS CUNICULUS (Rabbit)
Classification
Kingdom- Animalia
Phylum-Chordata
Sub-phylum- Vertebrata
Class- Mammalia
Order-Lagomorpha
Genus- Oryctolagus
Species- cuniculus
Comments
1. It lives in fields, making burrows (fossorial) and feeds on vegetation (herbivorous).
2. Its body is divided into head, neck and trunk and small bushy tail. The body is covered with hair of white brown or black colour.
3. The mouth is bounded by soft and fleshy upper and Lower lips. The upper lip is clefted (hair-lip) with sensory hair or wiskers on the snout.
4. Two large movable pinnae or external ears are present behind the eyes. The eyes are pink in colour.
5. The fore limbs are shorter and are used for burrowing.The hind limbs are long and help in leaping.
6. Sexes are separate with sexual dimorphism. The
females have mammary glands with nipples on the
abdomen. The males have a pair of testes in scrotal sac and a small and fleshy penis.


























0 Comments
Give me only suggestions and your opinion no at all Thanx